The great untapped potential of fish and fish chain co-products-such as sources of collagen and gelatin-is considered in a recent scientific review (Al-Nimry et al., 2021). (1) From a sustainable development perspective-with special regard to the goals of food security and circular economy-which will be applied, among others, in the #EcoeFISHent research project.
Collagen and gelatin
Collagen is a protein characteristic of the tissues of mammalian species. It is contained in connective tissue, bones, cartilage, tendons, skin and scales. Gelatin is in turn obtained from the degradation of collagen by its partial hydrolysis. Gelatins are produced by treating raw materials (with acids, bases or enzymes) and heating them in water, which precede extraction, filtration and drying.
Gelatin is characterized by affordability and high versatility of use (see next section). The overall demand, which is already significant as well as growing, is reflected in a production of jellies that is currently broken down as follows in relation to the various matrices:
– bovine. Cow hide and bones together express 52.5 percent of total production (with 29.4 percent and 23.1 percent, respectively),
– swine. Pig skin is still the most important raw material (46 percent),
– fish. In contrast, fish skin occupies only a minimal share, 1.5 percent. (2)
Industrial uses
Amino acid composition, level of whiteness (absence of color), gel strength and level of heavy metals are the key points for the use of gelatin and collagen in different industries:
– Feeding. Gelatin is often used as an ingredient because of its functional properties. To protect certain foods (e.g., meats, food preparations), with antimicrobial and antioxidant actions, in the form of biofilms. That is, as a stabilizer and thickener, to improve the texture of cheeses, baked goods and desserts,
– cosmetics. Hydrolysates are used in creams, lotions, shampoos, gels and other cosmetic products to improve their condition. As well as for skin care, due to their boasts of reducing UV radiation damage and acting as an anti-aging agent,
– drugs, dietary supplements, medical devices. Density and hardness of gelatins, in the production of coatings, can be modulated to affect the release rate of substances contained in capsules, gels, and dressing creams,
– biomedical applications. Collagen and gelatin are also used to repair and heal epidermal tissues. As well as for other uses related to antidiabetic, anticarcinogenic, antioxidant and antimicrobial properties,
– Other uses include the production of fertilizers, paints and coating films.
Fish jelly, what advantages
Jellies obtained from fish exhibit greater versatility (with structural and functional differences, between warm- and cold-water fish), compared with those of bovine and porcine origin. The lower melting point can be useful both for microencapsulation (of oils and vitamins, rather than flavors and dyes) and for rapid release of the contained substances. In contrast, their strength is significantly lower than that of mammalian gelatin. (3)
The use of gelatins of porcine and bovine origin, moreover, has some possible contraindications:
– nearly half of the planet’s population must abstain from the consumption of products derived from the slaughter of pigs-Muslims, approx. 2 billion, and Jews), and cattle (Hindus, more than 1.2 billion worshippers),
– collagen and cattle gelatines may be a vehicle for prions. Which are agents of bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE), still present in Brazil, and foot-and-mouth disease. (4)
#EcoeFISHent, research in Horizon 2020.
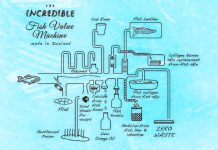
EcoeFISHent – the research project in Horizon 2020 in which our team is participating – deals, among other activities, with developing innovative methods for extracting collagen and gelatin, as well as peptides, Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids, and antioxidants from the waste of the seafood supply chain (fishing industry, aquaculture, large-scale distribution).
The extraction of collagen, gelatin and other various hydrolysates can enable the valorization of fishery processing wastes-through their ameliorative reuse, c.d.
upcycling
, such as ingredients in foods and dietary supplements, cosmetics and medical devices, and drugs-while reducing their impact on marine and aquatic ecosystems (5,6).
Dario Dongo and Andrea Adelmo Della Penna
Notes
(1) Al-Nimry et al. (2021). Cosmetic, Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Applications of Fish Gelatin/Hydrolysates. Marine Drugs 19:145, https://doi.org/10.3390/md19030145
(2) Alipal et al. (2021). A review of gelatin: Properties, sources, process, applications, and commercialization. Materialstoday: Proceedings 42(1):240-250, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.12.922
(3) Nitsuwat et al. (2021). Fish gelatin as an alternative to mammalian gelatin for food industry: A meta-analysis. LWT 141:110899, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2021.110899
(4) Nurilmala et al. (2021). Fish skin as a biomaterial for halal collagen and gelatin. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences (In press), https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.09.056
(5) Dario Dongo and Andrea Adelmo Della Penna. EcoeFISHent, upcycling and blue economy in the fish supply chain. The EU research project. GIFT(Great Italian Food Trade), 10/18/21, https://www.greatitalianfoodtrade.it/innovazione/ecoefishent-upcycling-e-blue-economy-nella-filiera-ittica-il-progetto-di-ricerca-ue
(6) SEE https://twitter.com/ecoefishent